Konbini, pillars of daily life in Japan
- GO TO JAPAN

- Dec 6, 2024
- 4 min read
Updated: Jan 21

In Japan, konbini (convenience stores) are much more than just neighborhood grocery stores. These ubiquitous establishments play a central role in the daily lives of Japanese people and constitute a true social phenomenon.
Konbini: a Japanese institution
Konbini are 24/7 convenience stores offering a wide range of products and services. The concept originated in Japan in the 1960s and quickly grew to become a national institution.
Seven-Eleven, Lawson and FamilyMart are the three main players in the market. Each of these chains has managed to differentiate itself by offering products and services adapted to the expectations of its customers.
Beyond food, konbini offer a multitude of services : paying bills, withdrawing money, sending parcels, renting DVDs, selling tickets, etc. They have also become places to meet and consume on site, in particular thanks to the establishment of catering areas.

A pioneer in the sector, Seven-Eleven is the largest konbini chain in Japan. It is renowned for:
From fresh produce to frozen products, including beauty products and stationery, Seven-Eleven offers a very comprehensive range.
Present in many countries, Seven-Eleven has been able to adapt its model to different markets.
The chain relies on a network of franchisees, which allows it to be very responsive to local needs.

Lawson is distinguished by:
Lawson offers higher quality products, often from organic or local farming.
Lawson collaborates with many brands to offer exclusive products.
The chain offers a range of healthy and balanced products (with a "well-being" focus).

FamilyMart is characterized by:
competitive prices, making it a preferred destination for budget-conscious consumers.
a warm and welcoming atmosphere in the stores.
The chain emphasizes the quality of fresh products, especially onigiris and bento.

Evolution of the number of stores by kombini brand in 2024
| Kombi chain | Jan-23 | Jan-24 | Variation |
1 | 21 111 | 21,248 | 0.65% | |
2 | 16,314 | 16,047 | -1.64% | |
3 | 13,735 | 13,779 | 0.32% | |
4 | 1,868 | 1,814 | -2.89% | |
5 | 1,169 | 1,173 | 0.34% | |
6 | 985 | 952 | -3.35% | |
7 | 340 | 345 | 1.47% | |
8 | 335 | 330 | -1.49% | |
9 | 219 | 209 | -4.57% | |
10 | 150 | 150 | 0.00% | |
11 | 128 | 126 | -1.56% | |
12 | 112 | 107 | -4.46% | |
13 | 65 | 63 | -3.08% | |
14 | 67 | 63 | -5.97% | |
15 | 45 | 49 | 8.89% | |
16 | TOMONY | 50 | 40 | -20.00% |
17 | 12 | 10 | -16.67% | |
56,705 | 56,505 | -0.35% |
The konbini market faces saturation: growth is sluggish
Despite their omnipresence in the Japanese urban landscape, konbini have experienced a slight decline in growth for four consecutive years.
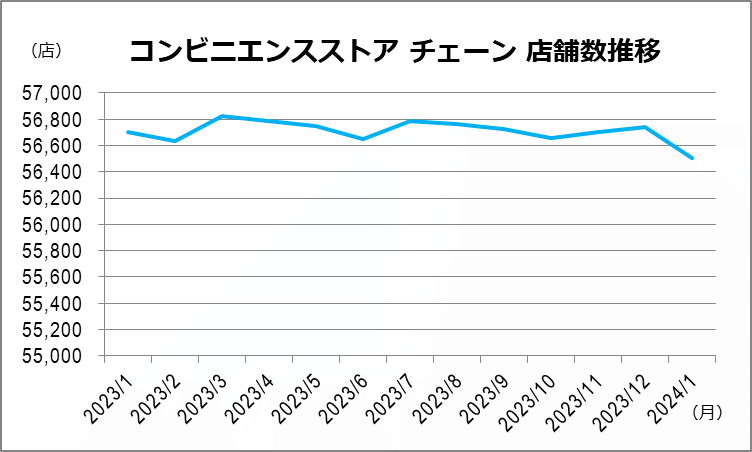
In fact, the total number of stores decreased by 0.35% between January 2023 and January 2024, marking a trend towards market stabilization.
This decline is explained by a progressive saturation of the market, particularly in large cities where the density of konbini is already very high. In addition, increased competition between the different chains, as well as the emergence of new distribution formats (e-commerce, home delivery), have pushed some players to close unprofitable stores.
While the total number of konbini is decreasing, not all chains are equal in the face of this trend.
The big winners: Seven-Eleven, Lawson and Seicomart slightly increased their number of stores, demonstrating their strong market positioning.
The case of FamilyMart!!: This brand, developed by FamilyMart Co., Ltd., is distinguished by rapid growth, with an increase of 8.89% in its number of stores. Its success is explained by its positioning in specific market segments, such as office buildings.
Losers: On the other hand, many chains, especially medium-sized ones, saw their number of stores decrease significantly. This is the case for TOMONY and La Mu Mart, which respectively recorded a decrease of 20% and 16.67% of their stores.
The reasons for these disparities are multiple:
Each chain has implemented different strategies to deal with market saturation. Some have focused on innovation, others on cost reduction, and still others on specialization.
Japanese consumers are increasingly demanding and are looking for personalized products and services. Chains that have been able to adapt to these new expectations have been more resilient.
The performance of each chain is also influenced by local factors, such as population density, local competition and market specificities.
Konbini: an economic model serving Japanese society
The success of konbini is based on a solid and adaptable economic model, which has profoundly transformed the consumption habits of the Japanese.
A virtuous economic model
Optimized logistics: Konbini have implemented extremely efficient logistics systems, allowing them to frequently renew their stocks and guarantee the freshness of their products. This rigorous organization allows them to adapt quickly to fluctuations in demand and to offer seasonal or current events products.
Responsiveness to trends: Konbini listen to consumers and do not hesitate to launch new products or services to meet their expectations. This ability to adapt allows them to remain competitive and build customer loyalty.
Digitalization: Digitalization is at the heart of the konbini strategy. More and more of them offer delivery services, online ordering and mobile applications, thus facilitating the consumer shopping experience.
A major societal impact. This successful economic model has significant repercussions on Japanese society:
Konbini have become places to live, work and play. They offer a wide range of services, from simply buying food to paying bills, renting DVDs or recharging phones.
Konbini create many jobs, particularly in the areas of logistics, sales and production. They thus contribute to the economic dynamism of cities and regions.
Konbini play an important role in the dissemination of Japanese popular culture. They have become meeting and exchange places, where consumers can discover the latest manga, magazines and derivative products.
Opportunities for foreign companies
A growing market: The Japanese konbini market is still growing, offering many opportunities for foreign companies.
Strategic partnerships: Foreign companies can form partnerships with major konbini chains to distribute their products in Japan.
Necessary cultural adaptation: To succeed in the Japanese market, it is essential to understand cultural specificities and adapt to the expectations of Japanese consumers.
Conclusion
Konbini, true institutions in Japan, have established themselves as key players in the economic and social landscape. Their success is based on constant adaptation to consumer needs, optimized logistics and a diversified service offering. However, the konbini market is currently experiencing a consolidation phase, marked by increased competition and gradual saturation. Companies wishing to establish themselves in Japan or develop their activities in this sector must demonstrate great agility and a deep understanding of the local market. Despite these challenges, the outlook remains promising for innovative players capable of offering differentiating concepts and meeting the expectations of an increasingly demanding clientele.



Comments